Tables
Create and manage structured data tables with defined schemas, data types, and constraints.
What is a Table?
A Table in a Knowledge Base is a structured container for your data with:
- Defined columns with specific data types
- Constraints like nullable, unique, and default values
- Comments for documentation
- PostgreSQL compatibility for familiar SQL operations
Creating Tables
Basic Table Creation
Creates a new structured table in a knowledge base - Defines a table schema with columns, data types, constraints, and documentation.
Resulting Table Schema
The code above creates a table with the following structure:
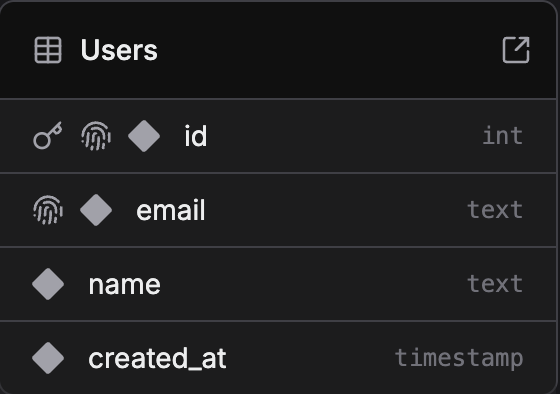
Column Properties
Each column can have the following properties:
| Property | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
name | str | The name of the column | Yes |
data_type | str | PostgreSQL data type (text, integer, decimal, boolean, timestamp, etc.) | Yes |
is_nullable | bool | Whether the column can contain NULL values | Yes |
is_unique | bool | Whether the column values must be unique | Yes |
default_value | str | Default value for the column (can use SQL functions like NOW()) | No |
comment | str | Description or comment about the column | No |
Supported Data Types
The following PostgreSQL data types are supported:
Integer Types
int- 32-bit integersmallint- 16-bit integerbigint- 64-bit integer
Text Types
text- Variable-length character stringsvarchar(n)- Variable character with length limit (e.g.,varchar(255))char(n)- Fixed-length character (e.g.,char(10))ltree- Hierarchical tree-like structures
Boolean Type
boolean- True/false values
Date/Time Types
date- Date onlytimestamp- Date and time (without timezone)timestamptz- Date and time with timezone
JSON Types
json- JSON datajsonb- Binary JSON data (more efficient)
Numeric Types
real- 32-bit floating pointdouble_precision- 64-bit floating pointnumeric(p,s)- Decimal with precision and scale (e.g.,numeric(10,2))
Importing Data
Import from Records
Takes a list of dictionaries and inserts them as rows in the specified table.
Table Structure: All fields from the first record determine the table structure. You cannot have different field sets per record - if the first record only has id, subsequent records with id and email will only show the id field.
This is what you'll see in the platform when importing records to your table.
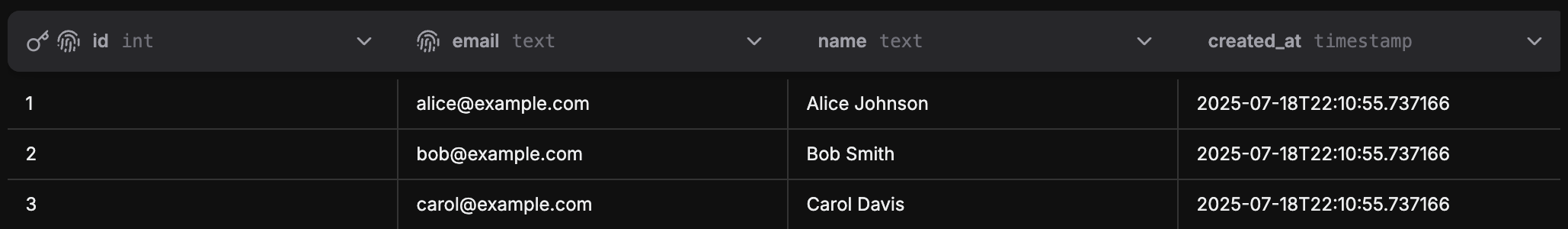
Import from CSV
Reads CSV files and loads the data into existing tables with schema validation.
The CSV file should have column headers that match your table schema:
Querying Data
SQL Queries
Executes SQL queries against knowledge base tables.
Important SQL Notes
- Table names are case-sensitive - Use double quotes around table names:
"Users" - PostgreSQL syntax - Use PostgreSQL-compatible SQL
- Escaping quotes - Use
\\'for single quotes in strings
Semantic Search
Performs semantic search on table data using embeddings, you have to specify which is the embedded column that you wanna search on.
For semantic search capabilities, you'll need to create embeddings first (see Embeddings)
Managing Tables
List All Tables
Returns metadata for all tables in the specified knowledge base.
Get Table Details
Retrieves the complete definition of a specific table - Returns table metadata including column definitions, constraints, and comments.
Get Table SQL Definition
Returns the exact SQL definition that would recreate the table.
Get All Tables SQL Definition
Returns the SQL definitions for all tables in the knowledge base.
Delete Table
Completely removes the table structure and data from the knowledge base.
Modifying Tables
Add Column
Adds a new column to an existing table.
Drop Column
Removes a column from an existing table.
Rename Column
Changes the name of an existing column.
Rename Table
Changes the name of an existing table.
Adding Constraints
Add Foreign Key
Creates a foreign key relationship between tables.
This creates a relationship between the two tables as shown:
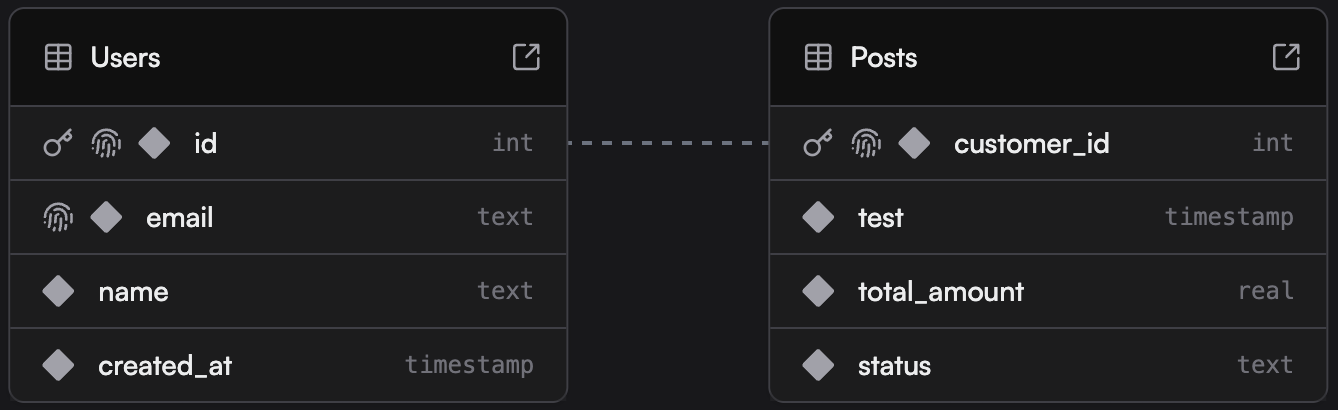
What happens with this constraint:
- Data integrity: You can only insert
customer_idvalues in Posts that exist asidvalues in Users - Cascade delete: When a User is deleted, all their Posts are automatically deleted too
- Referential consistency: The database ensures the relationship between tables is always valid
- Query optimization: The database can optimize joins between these tables more efficiently
Add Check Constraint
Adds a validation rule to ensure data meets specific conditions.
What happens with this constraint:
- Data validation: Every insert or update must satisfy the check condition
- Automatic rejection: Records that don't meet the criteria are automatically rejected
Add Unique Constraint
Ensures that values in specified columns are unique across rows.
What happens with this constraint:
- Uniqueness enforcement: No two rows can have the same combination of values in the specified columns
- Composite uniqueness: When multiple columns are specified, the combination must be unique (individual columns can still have duplicates)
Drop Constraint
Removes any type of constraint from a table.